Home
Services
Products
Projects
Who We Are
Blogs
Contact Us
Generative AI vs. Predictive AI: Understanding the Key Differences and Business Applications
The terms "Generative AI" and "Predictive AI" are increasingly prevalent in today's rapidly evolving technological landscape. As integral components of the broader ecosystem encompassing machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and robotics, they offer distinct functionalities, industrial applications, and benefits. Recent surveys indicate a significant upward trend in investment and implementation: 79% of enterprises plan to increase their Generative AI investment within the next year, while 75% consider predictive analytics crucial for their operations. These figures underscore the growing importance of both technologies.
While technical experts readily differentiate between these two AI branches, non-technical professionals often find the distinction less clear. The challenge lies not merely in defining Generative and Predictive AI, but in grasping their practical applications and potential use cases across various industries. Business strategists and executives must understand how these technologies can be integrated into their business models to drive growth and innovation.
Consider, for example, an e-commerce application. The core business value lies in customer data, product details, market sentiment, and other relevant information. To enhance sales, foster growth, and maintain competitiveness, effectively leveraging both Generative and Predictive AI is essential. Success hinges on identifying and capitalizing on the potential of AI within specific business operations.
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of Generative and Predictive AI, focusing on their distinct applications across diverse business niches.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science focused on imbuing machines with human-like intelligence. This is achieved through machine learning algorithms, deep learning techniques, natural language processing, and other cutting-edge technologies. The primary goal is to enable machines to learn, reason, and solve complex problems efficiently, mimicking human cognitive abilities.
AI models are trained on extensive datasets, enabling them to learn, adapt, and improve their performance. This data facilitates several key functions:
- Pattern Identification: AI models recognize patterns and relationships within data, enabling tasks like image recognition, conversational flow understanding, and trend analysis.
- Prediction: Learning from historical data allows AI models to forecast future outcomes, such as predicting stock prices or customer behavior.
- Decision-Making Refinement: Exposure to increasing amounts of data refines the decision-making capabilities of AI models, which is crucial for complex tasks like autonomous driving or medical diagnosis.
The type and volume of data used for training are critical. Image recognition models require labeled image datasets, while natural language processing models rely on text and code. Generally, more data leads to better performance, but data quality and diversity are equally important.
Returning to the e-commerce example, let's explore the applications of both Generative and Predictive AI. Generative AI can power chatbots to handle customer queries, improving customer experience and reducing the workload on support teams. Concurrently, Predictive AI can analyze customer and business data to provide insights into customer preferences, buying behavior, and engagement patterns, facilitating informed decision-making and enabling businesses to adapt to dynamic market conditions.
Generative AI vs. Predictive AI: A Comparative Overview
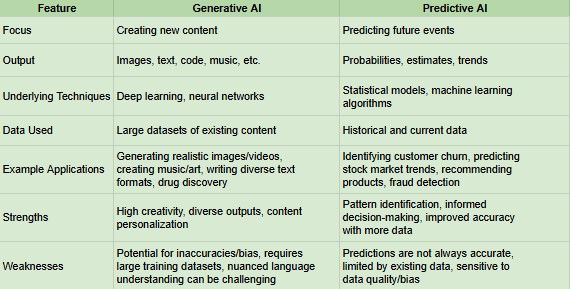
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI comprises algorithms capable of producing high-quality content ranging from text and code to images and music. These models effectively understand and process human language, generating coherent and natural-sounding output. Trained on extensive datasets, they learn language structure, word correlations, and semantic meaning, enabling the creation of new, contextually relevant content.
Businesses can fine-tune or further train these models for specific applications. Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) allows Generative AI models to access external knowledge bases, improving accuracy and relevance by reducing hallucinations and ensuring up-to-date information.
Key applications of Generative AI in business include content creation, personalized marketing, chatbot development, design exploration, prototyping, data augmentation, data summarization, personalized learning, and fraud detection.
What is Predictive AI?
Predictive AI models utilize algorithms that analyze historical data to forecast future outcomes. These models are trained on relevant data to identify hidden patterns and trends, providing organizations with valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Predictive AI leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze vast datasets from various sources, such as sales records, customer behavior, and market trends. By analyzing these patterns, the AI predicts future outcomes with a certain degree of accuracy.
Key applications of Predictive AI include demand forecasting, customer churn prediction, fraud detection and risk management, predictive maintenance, personalized marketing and sales, and dynamic pricing.
Conclusion
As AI continues to reshape the business world, understanding and leveraging both Generative and Predictive AI has become a strategic necessity. Generative AI enables organizations to automate content creation, enhance personalization, and drive innovation, while Predictive AI provides the data-driven insights needed to anticipate trends, optimize decisions, and improve performance.
At DEFX, we empower businesses to harness the full potential of both technologies through customizable, secure, and scalable AI solutions. Whether you’re looking to build intelligent assistants, automate workflows, or unlock actionable insights from your data, Defx provides the tools and expertise to help you lead in an AI-driven future.
By combining the creativity of Generative AI with the foresight of Predictive AI, forward-thinking companies can transform operations, elevate customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge. With Defx as your partner, the future of intelligent automation is within reach.
See More
Contact Us
Let’s make your Idea into Reality
Let's Talk
© Copyright DEFX. All Rights Reserved
GoodFirms ★ 4.2
Clutch ★ 4.2
Google ★ 4.2
